Last week’s official launch of What Would You Do? (WWYD) – our innovative new learning and development tool – was a resounding success, with half of the guests instantly arranging company demonstrations or further meetings.
Taking place in London on May 17th, the launch event welcomed around 50 representatives from major organisations in a variety of sectors, including finance, retail, transport, health, food, law, housing, packaging and public services. It was also great to see representatives of multinational companies, as our vision is to roll the game out not just in the UK but also abroad.
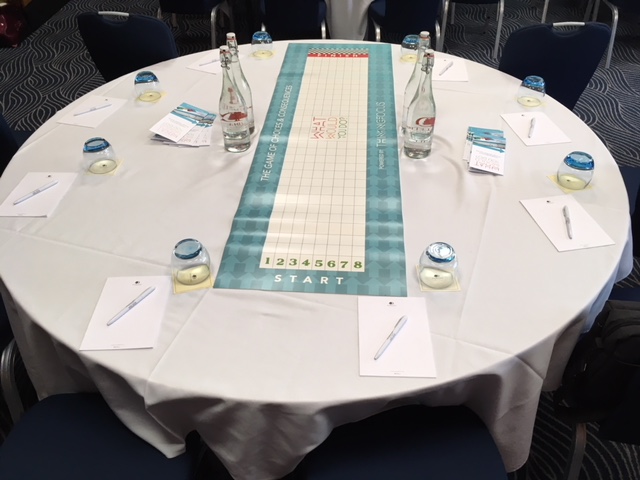
 The beauty of the launch event – and a big part of the reason for its success – was that WWYD is best appreciated when it’s played. It takes the form of a board game where participants aim to move up the board by getting points for correctly choosing the most appropriate answer to a variety of work-based dilemmas.
The beauty of the launch event – and a big part of the reason for its success – was that WWYD is best appreciated when it’s played. It takes the form of a board game where participants aim to move up the board by getting points for correctly choosing the most appropriate answer to a variety of work-based dilemmas.
But, as those at last week’s event quickly realised, the game itself is really a subterfuge: it creates a safe environment in which people can reflect on and discuss common issues, sharing experiences and learning from each other, as well as committing to new behaviour. When played between peers, it helps a team to discuss options and best practice, and highlights individuals’ gaps in skills and knowledge, or their management potential. When played cross-functionally, it can highlight incongruities or inconsistencies between different departments and managers across a company.
Playing the game
What Would You Do? gives maximum impact for minimum cost. As outcome-focused behavioural change experts, the team at Thinking Focus created WWYD to enable organisations not only to train their managers effectively but also to drive long-term culture change. Psychological concepts are woven into the game and, when played enough, the scenarios, debate and decisions can turn into learned behaviours which are then applied in the workplace.
The game includes 200 cards, each of which pose a different scenario covering one of eight management topics, to give variety, breadth and depth. The scenarios are split into two types: those which are set against the timer and require quick and test emotional decision-making, and those which are open to debate and result in more logical and rational decisions. The questions are designed to be as ‘grey’ as possible in order to generate the most discussion. Although there are no right or wrong answers, points are awarded for preferred answers.
Teams of up to eight people play the game, overseen by a facilitator. The facilitator role is key to the game, expanding the discussion, offering alternative suggestions, and even pointing out that the best option may not be one of the answers, or it may be a combination of them. Different companies with different cultures will also vary in their choice of the best response. For the launch event, Rob, Rich, Ricky and Graham acted as the facilitators with different teams.

It was fascinating to see how the role and background of each of our launch attendees influenced their answers to the scenarios posed in the WWYD questions. The majority of participants at the launch work in L&D or HR roles, but some are managers within other departments. It led to some interesting and insightful debate – which is exactly one of the main objectives of the game!
It was also great to see people not just talking about what they would do in hypothetical situations, but actually what they have done in similar, real work-based scenarios. There was much nodding of heads and even ironic laughter when some of the dilemmas were read out – showing us that people not only related to the hypothetical situations, but had actually in some cases dealt with something very similar. And, interestingly, some said they would choose one answer, but when the situation arose in real life, they had actually done something different.
The response
The feedback from our guests was brilliant! Here are just a few of their comments:
“I like the simple approach that gives the opportunity for quite deep thinking and discussion.”
“It’s a good tool and catalyst to start conversations.”
“I like the flexibility of it, you can use it at all different levels, flex it to your own business. It’s as useful on the shop floor as it is in the boardroom.”
“It creates genuine conversations, not pseudo conversations.”
“I can’t compare it to anything else really. It’s very interactive.”
“It’s the discussion and the result that’s important.”
“An organisation needs to know the way their managers work things out, and ask: Do we want to keep doing it this way or does this show us that we need to change?”
Inspiration

The launch also heard from Sonia Belfield, Adient’s HR director for Northern Europe. She described how she inspired us to create WWYD and how it has been trialled across her organisation to great success.
She said: “Team leaders are the most fundamental people in our business because they manage the vast majority of people that we employ. For me, WWYD is about helping people to be able to have conversations that make them better managers.”
The facilitator is key
The role of the facilitator is critical to the game, enabling rich discussion between the players. In the wrong hands, people could just end up playing the game and not learning from it. That’s why we give guidance on selecting the right people in an organisation to act as facilitators, as well as offering facilitator training as part of the WWYD package.
Facilitator training takes approximately five hours, and offers guidance on how to make the most of setting the game up correctly and the dynamics of managing the gameplay in the best way possible.
There are some real subtleties about the scenarios, so facilitators need to be able to listen to the answers that are coming back and give reinforcement of any good answers. The training aims to give the facilitator the confidence to be able to deal with different conversations, as well as how to manage the players (for example, how do you deal with the person who doesn’t get involved, or the one who always waits until the others have answered?)
The game also includes a facilitator’s handbook, which includes a debrief of each scenario and offers suggestions for discussion.

Interesting questions
Our launch guests had a variety of questions about the thinking behind the game, and its application within the workplace.
But they also asked about various areas of development, some of which we are already working on, and others which gave us new ideas.
How do you keep the game up-to-date and relevant?
All the scenarios we have created are as valid today as they were 10 or 20 years ago, and they will continue to be so for years to come. But we are looking at adding scenarios based on other issues, such as diversity and inclusion.
We’re also keen to investigate the development of a digital version of the game and – directly prompted by a question at the launch event – will be looking at training facilitators online.
We also intend to create a facilitator community, where facilitators of WWYD can share experiences, issues and ideas with other facilitators from other organisations.
Does it fit in hand luggage on the plane?
This was quite possibly the most unexpected question of the day – although it’s very relevant to organisations with international offices!
The answer is that the fully-boxed version will only fit in the hold – and it’s robust enough to do so – but that flexibility over how the game is played means that the key pieces can easily be packed in to hand luggage.
And finally…
Well, what a great start! We’re now busy following up on all those requests for more information and demos, including some from organisations who weren’t able to attend the launch but are nonetheless intrigued by the benefits that WWYD could bring.
Why not contact us to see what all the fuss is about? Or read more about WWYD: how the game was created, the thinking behind it, and how it works in practice.