As a leader, you cast a shadow. It may be unintentional, but it is inevitable. In your role as the ‘boss’, the ‘Grand Fromage’ (big cheese), the top banana, you create a range of perceptions for people that casts a shadow. A shadow is made up of a collection of helpful and unhelpful thoughts, it’s the lens through which your people attempt to interpret what you stand for and what you really want from them. Your shadow is how you are seen and become known – it’s your reputation.
A shadow is made up of a collection of helpful and unhelpful thoughts, it’s the lens through which your people attempt to interpret what you stand for and what you really want from them.
Leadership shadows can be fantastic, but they can also be destructive.
Let’s consider a leadership shadow that isn’t working. You, the person, may be reasonable (well, most of the time) and impatient—yes, but reasonable. You hired your people to do a job, but they are not stepping up for some reason. If your shadow creates doubt or uncertainty in your people, they will look for reassurance that they are doing a good job and getting it right.
Your tendency, though, is to step in and poke around to get the confidence and reassurance you need that they have it covered. So, when you lack confidence and need reassurance, you poke further, ask more searching questions, and start to dig deeper.
Do you see the problem? You both want confidence and reassurance.
But, if your leadership shadow causes uncertainty, you will unlikely get the confidence and reassurance you crave. When your people feel uncertain, they may pause and not want to expose a perceived weakness; you are their boss! As the boss, you decide people’s future. People don’t want to give their boss any cause for concern. And so, inertia reigns; they pause, fret, slow down, and, inevitably, are scared to fail.
When your people feel uncertain, they may pause; they may not want to expose a perceived weakness.
And so, the perpetual cycle begins as they wait for the leader to provide direction and guidance; as the boss, you feel the need to check and search for comfort. This feeling leads to resentment; as people start to question your trust and faith in them, you as the leader start to question whether your team are up to it; you’re not seeing them stepping up!

Photo by Ian Keefe on Unsplash
We call this the leadership vacuum; it emerges as a void between leaders and their reports. Learned helplessness leads to inertia and causes frustration. Leaders want their people to step up, and direct reports often want their leaders to set the directions and get out of their way.
The solution to this problem requires a change in behaviours from both.
As a leader, you need to create the headroom for your people to step up. That means being prepared to give before taking, and trusting your people. When you trust people and communicate that trust clearly and openly, you can begin the dialogue and establish the behaviours that fill the vacuum — creating safety where people can fail safely and not question themselves about their own self-worth in your eyes as their leader. To paraphrase Brene Brown, author of Dare to Lead, ‘let’s teach them to land before you ask them to jump’. This environment of trust enables learning and creates the space to test assumptions and expectations without concern.
When you trust people and communicate that trust clearly and openly, you can begin the dialogue and establish the behaviours that fill the vacuum.
In this podcast, Richard and Ricky explore what this means. What is different about the way in which senior people need to think, and what does that mean for them and the way that they work?
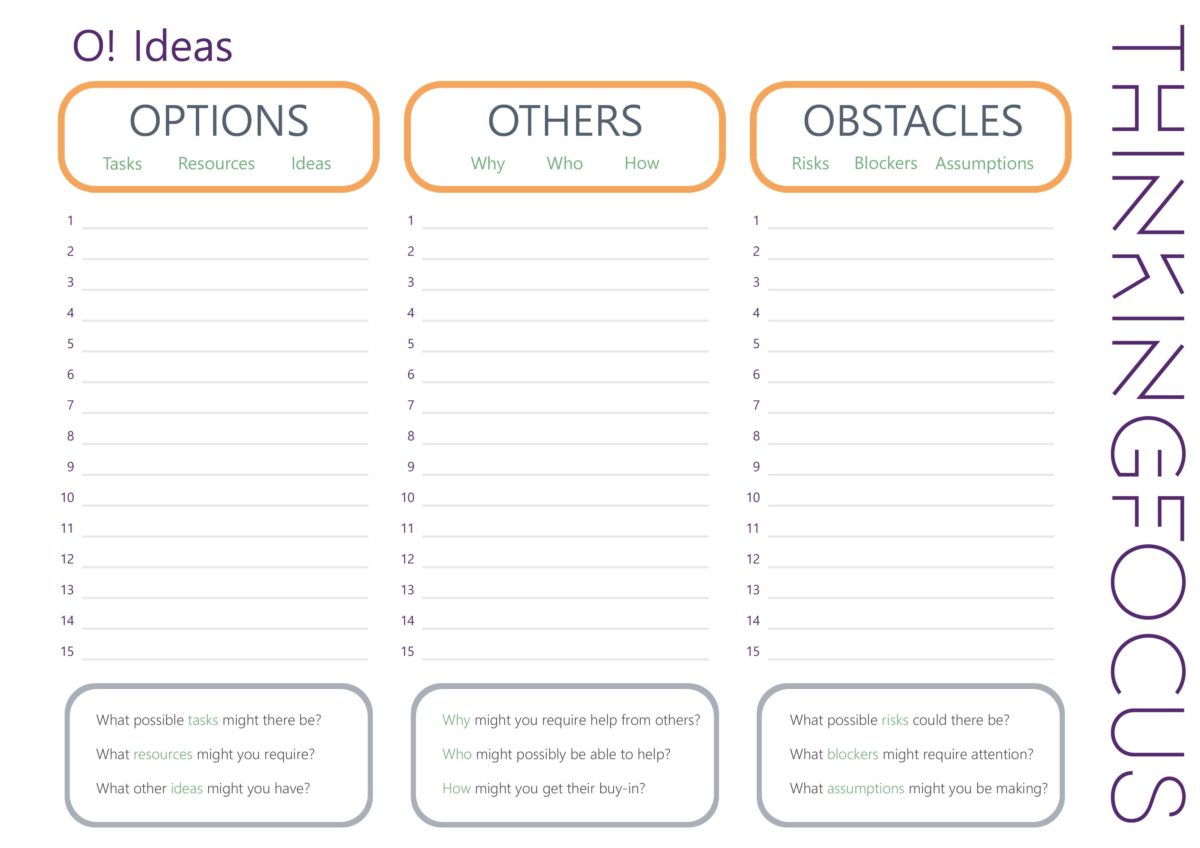
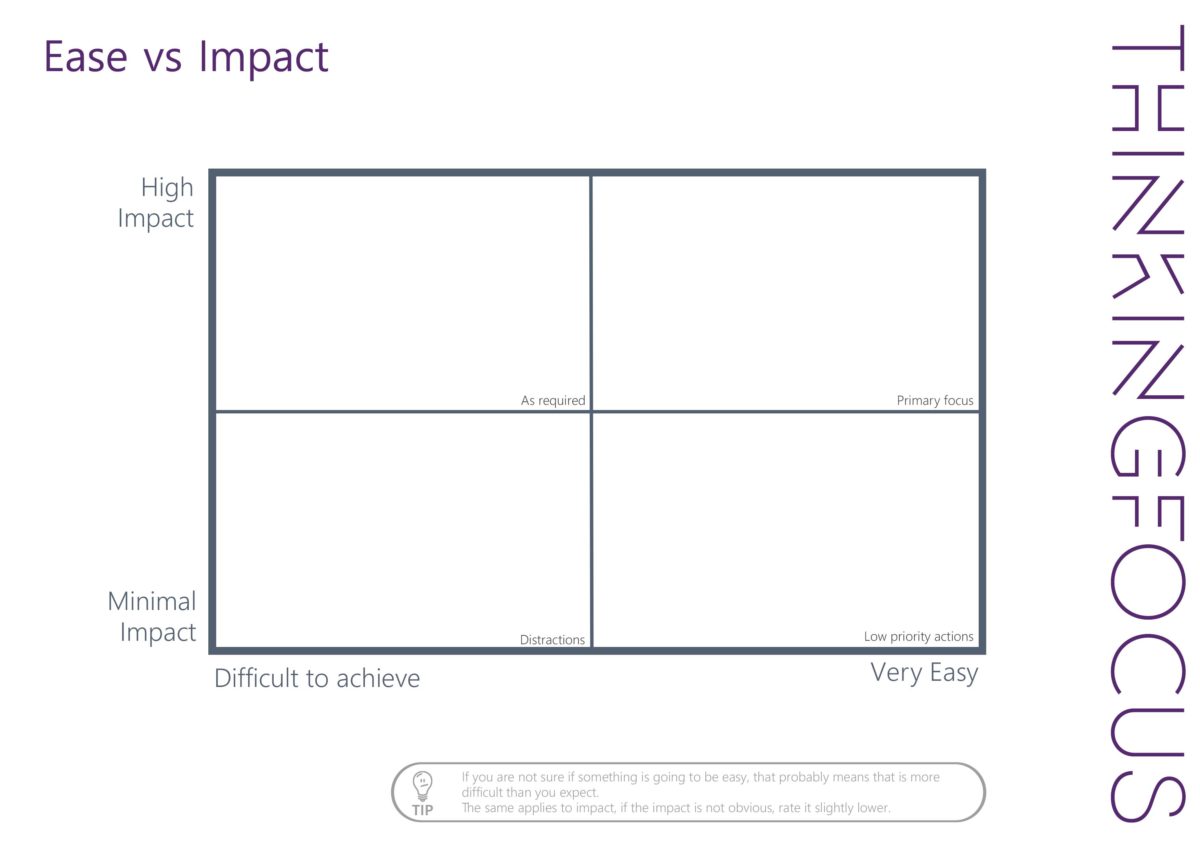
You can find out more about the four areas and how we use them below:
Your people need to step into the void and take a risk, enter the growth zone and trust you to have their backs. This leap, however, won’t happen until you put your trust in them. Until you communicate clearly about what you expect and work together to define how they might do it, and then crucially, get out of their way and let them get on with it.
Whichever role you’re in, it takes a leap of faith. It will take some coaching, regular discussion, and check-ins. You’re both looking for new behaviours that provide you with confidence and reassurance for it to become your new normal. It will take a little time to change your “go-to” behaviours of poking around to look for the certainty you need.
But, as with most things, if you want your people to step up – that journey begins with you!
Thinking Focus are behavioural change experts in the workplace. We believe that individuals, teams and business units underperform, not by choice, but because they can’t get out of their own way. We help individuals, teams, and business units challenge mindsets to unlock untapped and hidden potential and become more effective and productive.