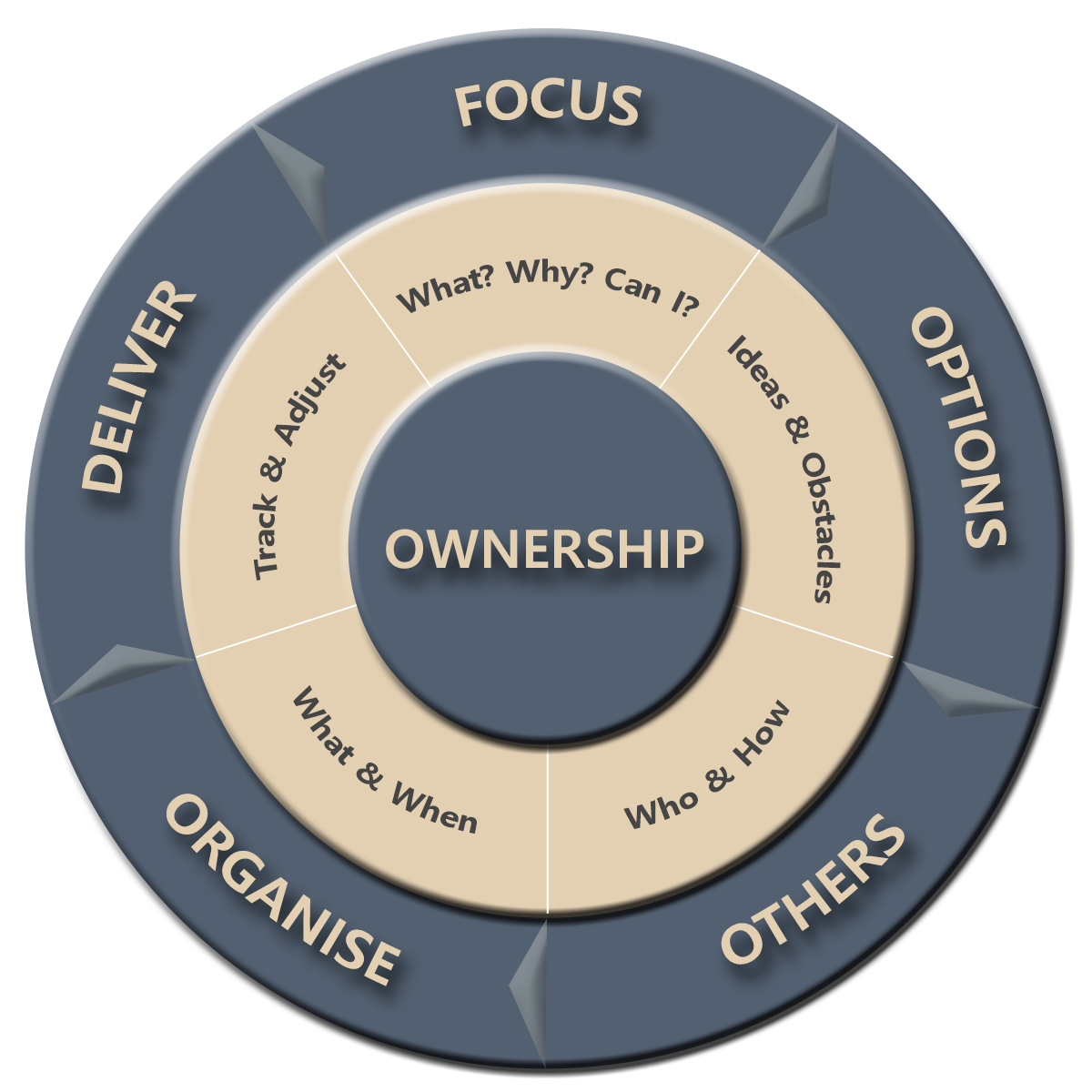
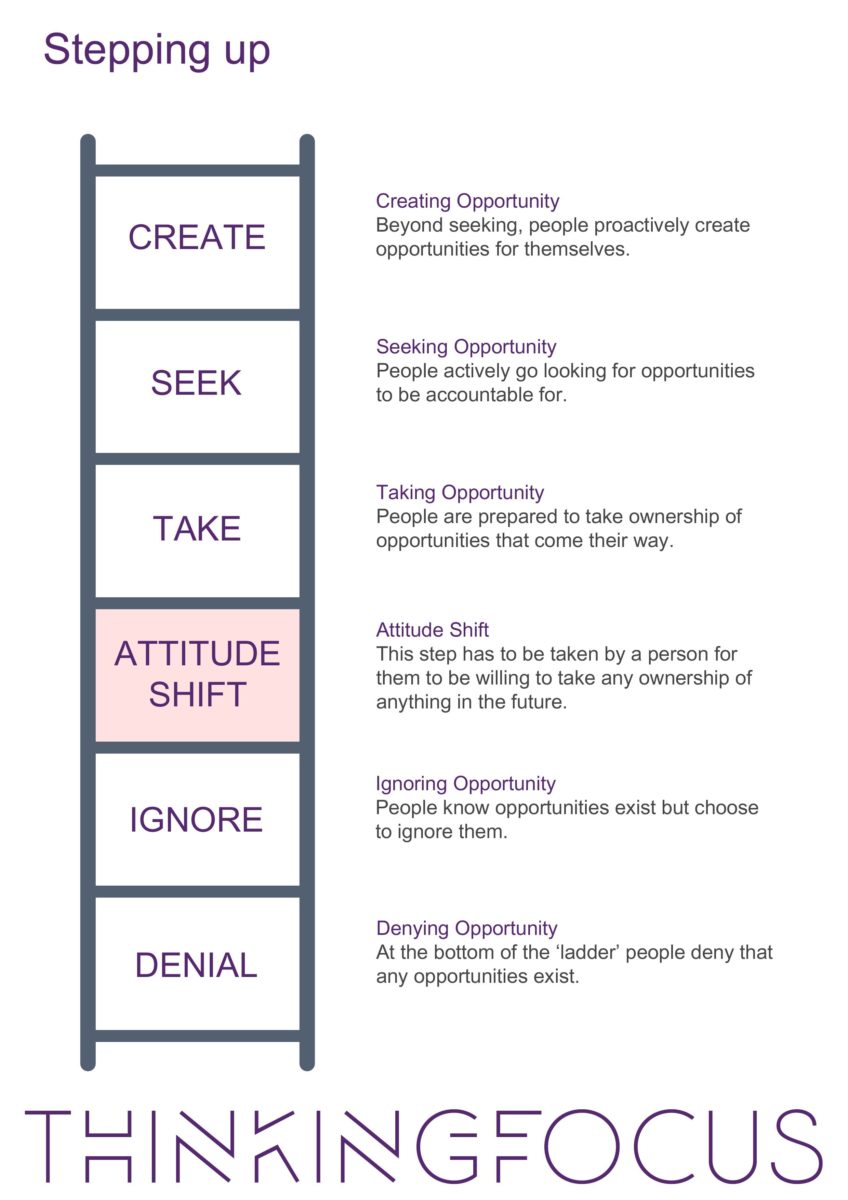
Try the Benchmark Method
New Year’s resolutions will be on the minds of lots of people; if that’s the case, if you’re serious, you need to get goal setting.
A lot of the time, New Year’s resolutions focus on feelings and confidence, and SMART goals don’t work for something subjective, not until now, that is. SMART goals are great for goal setting, when you know how to set goals using SMART they’re awesome, but what do you do when the subject of your goal is a feeling, a perception or a judgement, something subjective, well we have the perfect solution with benchmark goal setting.
You can take something that is hard to measure and turn it into something that will work with a SMART goal. SMART goals are essential to the Thinking Focus Toolkit for Team Leaders and Managers.